Wikipedia Spreading Activation
Aug 14, 2014 - Spreading Activation Model and Wikipedia activation model of semantic networks within Wikipedia s hyperlink structure to describe.
Spreading activation is a method for searching associative networks, neural networks, or semantic networks. The search process is initiated by labeling a set of source nodes e.g. concepts in a semantic network with weights or activation and then iteratively propagating or spreading that activation out to other nodes linked to the source nodes. Most often these weights are real values that decay as activation propagates through the network. When the weights are discrete this process is often referred to as marker passing. Activation may originate from alternate paths, identified by distinct markers, and terminate when two alternate paths reach the same node. However brain studies show that several different brain areas play an important role in semantic processing, 1
Spreading activation models are used in cognitive psychology 2 3 to model the fan out effect.
Spreading activation can also be applied in information retrieval, 4 5 by means of a network of nodes representing documents and terms contained in those documents.
Contents
1 Cognitive Psychology
2 Algorithm
3 Examples
4 See also
5 Notes
6 References
7 External links
Cognitive Psychology edit
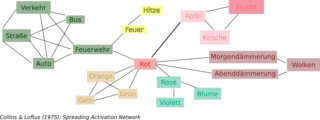
As it relates to cognitive psychology, spreading activation is how the brain moves through an entire network of ideas to retrieve specific information. The spreading activation theory presents the array of concepts within our memory as cognitive units, each consisting of a node and its associated elements or characteristics, all connected together by lines. 3 A spreading activation network can be represented schematically, in a sort of web diagram with shorter lines between two nodes meaning the ideas are more closely related and will typically be associated more quickly to the original concept. 2
When a word the target is preceded by an associated word the prime in word recognition tasks, participants seem to perform better in the amount of time that it takes them to respond. For instance, subjects respond faster to the word doctor when it is preceded by nurse than when it is preceded by an unrelated word like carrot. This semantic priming effect with words that are close in meaning within the cognitive network has been seen in a wide range of tasks given by experimenters, ranging from sentence verification to lexical decision and naming. 6
As another example, if the original concept is red and the concept vehicles is primed, they are much more likely to say fire engine instead of something unrelated to vehicles, such as cherries. If instead fruits was primed, they would likely name cherries and continue on from there. The activation of pathways in the network has everything to do with how closely linked two concepts are by meaning, as well as how a subject is primed.
Algorithm edit
A directed graph is populated by Nodes 1N each having an associated activation value A i which is a real number in the range 0.0 1.0. A Link i, j connects source node i with target node j . Each link has an associated weight W i, j usually a real number in the range 0.0 1.0. 7
Parameters:
Firing threshold F, a real number in the range 0.0 1.0
Decay factor D, a real number in the range 0.0 1.0
Steps:
Initialize the graph setting all activation values A i to zero. Set one or more origin nodes to an initial activation value greater than the firing threshold F. A typical initial value is 1.0.
For each unfired node i in the graph having an activation value A i greater than the node firing threshold F:
For each Link i, j connecting the source node i with target node j , adjust A j A j A i W i, j D where D is the decay factor.
If a target node receives an adjustment to its activation value so that it would exceed 1.0, then set its new activation value to 1.0. Likewise maintain 0.0 as a lower bound on the target node s activation value should it receive an adjustment to below 0.0.
Once a node has fired it may not fire again, although variations of the basic algorithm permit repeated firings and loops through the graph.
Nodes receiving a new activation value that exceeds the firing threshold F are marked for firing on the next spreading activation cycle.
If activation originates from more than one node, a variation of the algorithm permits marker passing to distinguish the paths by which activation is spread over the graph
The procedure terminates when either there are no more nodes to fire or in the case of marker passing from multiple origins, when a node is reached from more than one path. Variations of the algorithm that permit repeated node firings and activation loops in the graph, terminate after a steady activation state, with respect to some delta, is reached, or when a maximum number of iterations is exceeded.
Examples edit
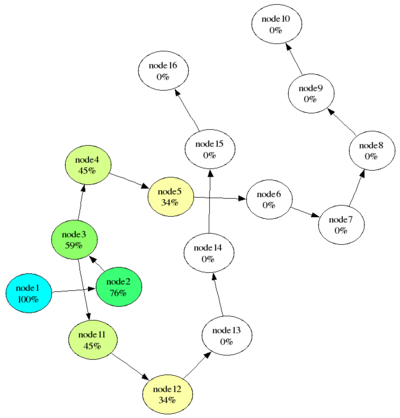
In this example, spreading activation originated at node 1 which has an initial activation value of 1.0 100. Each link has the same weight value of 0.9. The decay factor was 0.85. Four cycles of spreading activation have occurred. Color hue and saturation indicate different activation values.
See also edit
Connectionism
Notes edit
Karalyn Patterson, Peter J. Nestor Timothy T. Rogers: Where do you know what you know. The representation of semantic knowledge in the human brain 1
a b Collins, Allan M.; Loftus, Elizabeth F., A spreading-activation theory of semantic processing, Psychological Review. 1975 Nov Vol 82 6 407-428 2
a b John R. Anderson. A spreading activation theory of memory. Journal of Verbal Learning and Verbal Behavior, 1983
S. Preece, A spreading activation network model for information retrieval. PhD thesis, University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign, 1981.
Fabio Crestani. Application of Spreading Activation Techniques in Information Retrieval. Artificial Intelligence Review, 1997
Chwilla, Dorothee J.; Hagoort, Peter; Brown, C. M., The mechanism underlying backward priming in a lexical decision task: spreading activation versus semantic matching, The Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 1998, 51A 3, 531-560 3
Boosting item keyword search with spreading activation Aswath, D.; Ahmed, S.T.; Dapos;cunha, J.; Davulcu, H., Web Intelligence, 2005. Proceedings. The 2005 IEEE/WIC/ACM International Conference on Volume, Issue, 19-22 Sept. 2005 Page s : 704 - 707
References edit
Nils J. Nilsson. Artificial Intelligence: A New Synthesis. Morgan Kaufmann Publishers, Inc., San Francisco, California, 1998, pages 121-122
Rodriguez, M.A., Grammar-Based Random Walkers in Semantic Networks, Knowledge-Based Systems, 21 7, 727-739, doi:10.1016/j.knosys.2008.03.030, 2008.
Karalyn Patterson, Peter J. Nestor Timothy T. Rogers Where do you know what you know. The representation of semantic knowledge in the human brain, Nature Reviews Neuroscience 8, 976-987 December 2007
External links edit
JMaPSS The Java Marker-Passing Search Service, a relevance search engine employing a family of marker-passing algorithms based on spreading activation theory.
Texai An open source project to create artificial intelligence that provides a Java spreading activation class library.
Retrieved from Spreading_activation oldid 630328482
Categories: SemanticsPsycholinguisticsMemoryArtificial intelligenceAlgorithmsSearch algorithms.
Measuring Conceptual Similarity by Spreading Activation over. Wikipedia s Hyperlink Structure. Stephan Gouws, G-J van Rooyen, and Herman A. Engelbrecht.
Connectionism is a set of approaches in the fields of artificial intelligence, cognitive psychology, cognitive science, neuroscience, and philosophy of mind, that.

Various experiments supported the theory that activation spreading among related ideas was the best explanation for the facilitation observed in the lexical.
Spreading activation is a method for searching associative networks, neural networks, or semantic networks. The search process is initiated by labeling a set of.
Spreading activation is a method for searching associative networks, neural networks, or semantic networks. The search process is initiated by labeling a set of Cognitive Psychology - Algorithm - Examples - See alsoConnectionism - Wikipedia, the free encyclopediahttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ConnectionismCachedJump to Spreading activation - edit. Main article: Spreading activation. In most connectionist models, networks change over time. A closely related and.